Countless times a day, seabirds dive-catch prey from the ocean, boats enter the water from dry land, and seaplanes touch down gently amid the waves. The phenomenon of objects entering water is commonplace, yet a full understanding of the physics of water entry remains elusive, especially as it pertains to instances where a solid object enters a body of water that contains other solid objects, such as a gull diving into a rocky patch of sea.
A team of researchers at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering is exploring this relatively untouched area of research and has published a series of surprising findings that may lead to strategies for minimizing the strain of water entry on marine vessels, seaplanes, and space-crew capsules designed for water landing.
“Many studies of water entry overlook the presence of solid, stationary objects like ice or rocks in the water, and it is clear that these items can affect objects entering the water and change the physics of impact,” said Maurizio Porfiri, professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at NYU Tandon and lead author of the paper “Solid Obstacles Can Reduce Hydrodynamic Loading During Water Entry,” which appears in the journal Physical Review Fluids. Porfiri’s collaborators include NYU Tandon Adjunct Faculty Member Ghania Benbelkacem, in the Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, and Mohammad Jalalisendi, a recent doctoral degree graduate in Porfiri’s group.
Porfiri and his collaborators in the Dynamical Systems Laboratory created an experiment using a solid wedge plunging into a tank of water containing a neutrally buoyant cylinder. Sensors in the setup measured acceleration, pressure, and depth, and the team used particle image velocimetry to visualize flow and measure the speed of water jets produced by the wedge as it hit the water. Analyses revealed that the cylinder’s presence in the water dramatically changed the physics of impact on the wedge in unexpected ways.
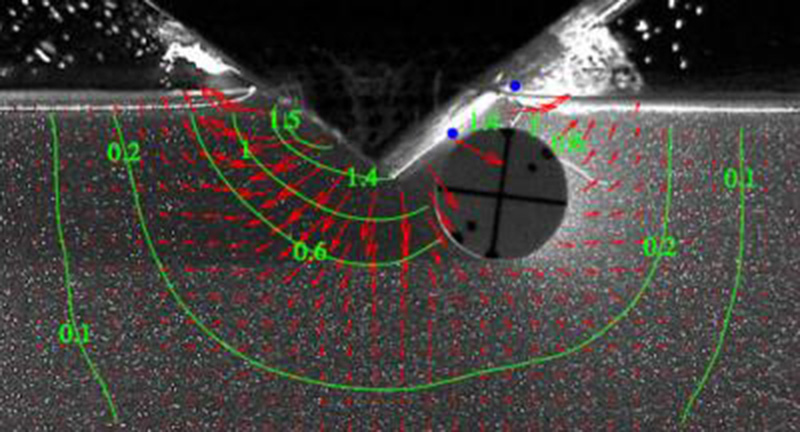
Through experiments and theory, NYU Tandon researchers illustrate surprising changes in water pressure on a wedge that strikes the water (upper right) when an object — the buoyant cylinder near the wedge — is present. While the team measured an increase of water pressure in the region nearest the cylinder, they discovered decreased water pressure in the pileup region (outflow). The red arrows indicate the direction and speed of the water particles, and the green lines indicate contour plot of the velocity magnitude of the water particles. Blue dots mark the location of the sensors.
To the researchers’ surprise, they noted a decrease in pressure in the pile-up — the region of the fluid where a high-speed jet is produced as the wedge lands– on the side of the wedge closest to the cylinder. Porfiri and the team attributed this decrease to the cylinder confining fluid on that side, so that less water was displaced upon impact. However, in a contradictory finding, the team noted an increase in pressure toward the wedge’s keel, indicating a rich, complex effect from the cylinder. Further studies are needed to reconcile these conflicting findings, but the researchers note the importance of continuing to explore the interplay between stationary items in water and objects entering the water.
“It is clear that there are sympathetic interactions between these objects, and as we gain a better understanding of them, it may lead to designs and materials that mitigate some of the strain on marine vessels that travel in occluded waters, especially those exploring and navigating polar regions,” said Porfiri.
Filed Under: Rapid prototyping




