An aluminum alloy developed in the 1940s has long held promise for use in automobile manufacturing, except for one key obstacle. Although it’s nearly as strong as steel and just one-third the weight, it is almost impossible to weld together using the technique commonly used to assemble body panels or engine parts.
That’s because when the alloy is heated during welding, its molecular structure creates an uneven flow of its constituent elements—aluminum, zinc, magnesium and copper—which results in cracks along the weld.
Now, engineers at the UCLA Samueli School of Engineering have developed a way to weld the alloy, known as AA 7075. The solution: infusing titanium carbide nanoparticles—particles so small that they’re measured in units equal to one billionth of a meter—into AA 7075 welding wires, which are used as the filler material between the pieces being joined. A paper describing the advance was published in Nature Communications.
Using the new approach, the researchers produced welded joints with a tensile strength up to 392 megapascals. (By comparison, an aluminum alloy known as AA 6061 that is widely used in aircraft and automobile parts, has a tensile strength of 186 megapascals in welded joints.) And according to the study, post-welding heat treatments, could further increase the strength of AA 7075 joints, up to 551 megapascals, which is comparable to steel.
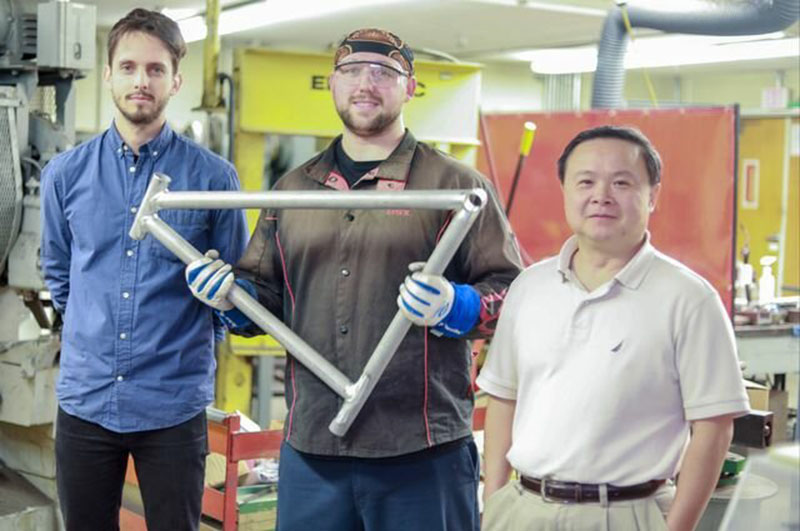

Graduate student Maximilian Sokoluk; laboratory mechanician Travis Widick, holding a demonstration bike frame welded using aluminum alloy 7075; and Professor Xiaochun Li. Credit: Kenny Stadelmann/UCLA
Because it’s strong but light, AA 7075 can help increase a vehicle’s fuel and battery efficiency, so it’s already often used to form airplane fuselages and wings, where the material is generally joined by bolts or rivets rather than welded. The alloy also has been used for products that don’t require joining, such as smartphone frames and rock-climbing carabiners.
But the alloy’s resistance to welding, specifically, to the type of welding used in automobile manufacturing, has prevented it from being widely adopted.
“The new technique is just a simple twist, but it could allow widespread use of this high-strength aluminum alloy in mass-produced products like cars or bicycles, where parts are often assembled together,” said Xiaochun Li, UCLA’s Raytheon Professor of Manufacturing and the study’s principal investigator. “Companies could use the same processes and equipment they already have to incorporate this super-strong aluminum alloy into their manufacturing processes, and their products could be lighter and more energy efficient, while still retaining their strength.”
The researchers already are working with a bicycle manufacturer on prototype bike frames that would use the alloy; and the new study suggests that nanoparticle-infused filler wires could also make it easier to join other hard-to-weld metals and metal alloys.
Filed Under: Product design