
Image credit: NASA
On Nov. 7 NASA tested potential satellite sensors that could be used to measure atmospheric composition, air quality, and the health of the ocean. The Aerosol Characterization from Polarimeter and Lidar (ACEPOL) project was used to test instruments that could fly as part of the Aerosol-Cloud Ecosystem (ACE) study. The sensors were flown on board the ER-2 high altitude craft over California. This suite of sensors includes four polarimeters, differing from one another in size, angle, and the technique used to measure and record data. Each will then be examined to find out how the differences manifest during data collection.
The video, from March 2016, shows the first flight of the ER-2.

Image credit: NASA
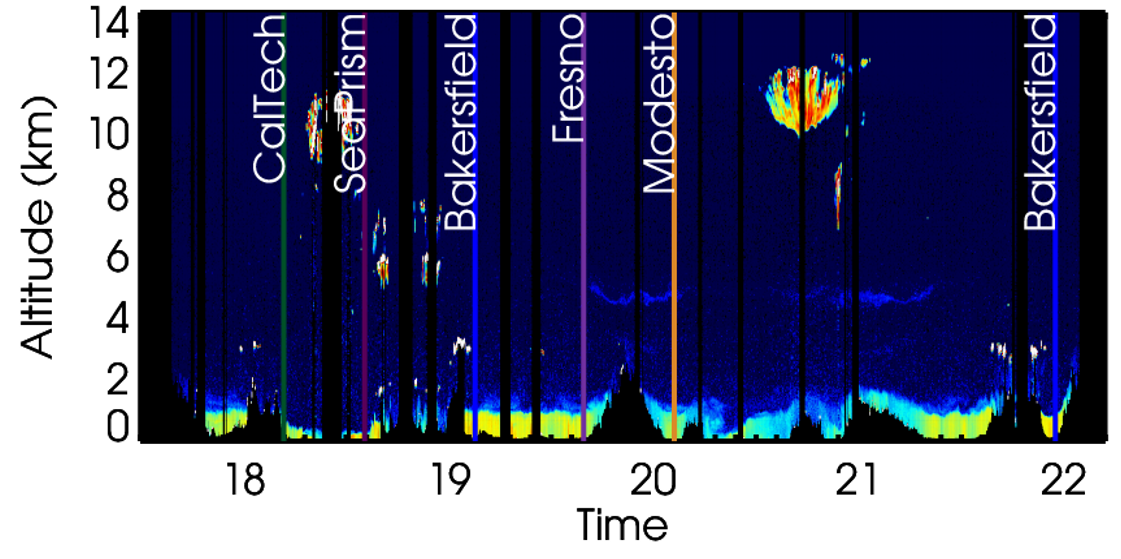
Data collected during the Nov. 7 flight. NASA explains it this way: ” The ground is black, dark blue indicates clear air, white indicates water clouds. Transparent cirrus clouds high in the atmosphere show up in yellow and orange colors. Yellow, green and blue colors at lower altitudes indicate aerosol.” Image credit: NASA / Sharon Burton
Filed Under: Aerospace + defense




