The ASTM standards organization has a definition for sheet lamination– an additive manufacturing process in which sheets of material are bonded to form an object. 3D printing /additive manufacturing continues to evolve, so there are several variations on lamination. Some of the names, however, are more about branding than a different additive technology.
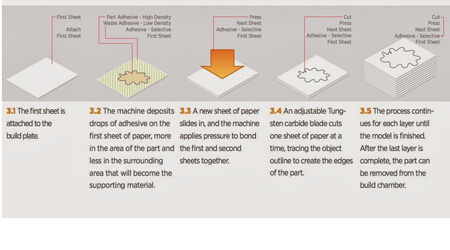
Sheet lamination is the use of sheets of some material that are bound with a glue or fused with an electrical process to form an object.
Selective Deposition Lamination refers to the ability to selectively apply a binding substance, or heat and pressure to adhere layers of material.
Ultrasonic Additive Manufacturing is a variation of sheet lamination in that it uses ultrasonic vibrations to bind different materials into a solid object.
Laminated Object Manufacturing is one of the first names for this technology. Like sheet lamination, it uses layers of a material, such as paper for plastic. However this method binds the sheets using heat and pressure. Then another process, such as a laser or a knife blade is used to cut the solidified layers into the desired shape.
Selective Lamination Composite Object Manufacturing is the latest version of lamination. This technique builds composite parts using layer-by-layer laminated thermoplastic composite fabric sheets from a roll. This process uses a range of custom-made thermoplastic reinforced unidirectional or multidirectional woven fibers. Some of the composite matrix materials include woven glass fiber, woven carbon fiber, or other woven aramid fibers reinforced with a choice of Nylon 6, Nylon 11, Nylon 12, Peek, Pekk, Polycarbonate, and others. The composites can be tailored for exceptional toughness, environmental resistance, vibration dampening, low flammability characteristics, high wear resistance and high strength to weight ratio.
As of this post, the companies that supply lamination 3D printing include Mcor Technologies, Fabrisonic and EnvisionTEC.
Filed Under: Rapid prototyping, Make Parts Fast