According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), electric motors are responsible for half the energy use in the U.S. manufacturing sector, and the International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that electric motor-driven system account for more than 40 percent of global electricity consumption.
To promote energy savings, increase efficiency, and reduce operating costs for manufacturing operations, many countries and regions around the world have established minimum efficiency performance standards (MEPS) for motors used in industrial, commercial, and residential applications. The ability to establish and enforce MEPS, however, depends on a standardized testing and classification system for motor efficiency.
The U.S. began regulating electric motor efficiency in 1992 with the “Energy Efficiency Provision” of the Energy Policy Act (EPAct), and in 1997, the U.S. was the first country to establish MEPS for electric motors. These regulations, however, only applied to motors manufactured in or sold to U.S. markets, with many countries around the world operating under their own efficiency rating systems and MEPS for electric motors.
To harmonize efficiency classifications for motors manufactured and sold in the global market, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) introduced the standard IEC 60034-30 : 2008, which was updated in 2014 and is now referred to as to IEC 60034-30-1 : 2014, “Rotating electrical machines – Part 30-1: Efficiency classes of line operated AC motors.”
In addition to defining efficiency classes for electric motors, the IEC has also developed a standard that specifies how to determine motor efficiencies and losses based on established testing methods. This standard, IEC 60034-2-1 : 2014, provides the basis for defining the efficiency classes in IEC 60034-30-1.
Both standards were developed in conjunction with the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), the Japan Electrical Manufacturers Association (JEMA), and the European Committee of Manufacturers of Electrical Machines and Power Electronics (CEMEP).
Motors that fall under IEC 60034-30-1
The IEC standard 60034-30-1 : 2014 applies to motors that meet the following criteria:
- single speed induction or permanent magnet type motors (single- and three-phase) operated on a sinusoidal mains supply
- frequencies of 50 or 60 Hz
- 2, 4, 6, or 8 poles
- rated output from 0.12 kW to 1000 kW
- rated voltage from 50 V to 1000 V
- capable of continuous operation at rated power without exceeding the specified insulation class (S1, continuous, duty)
- ambient operating temperature between -20° C and +60° C
- operating altitude up to 4000 m above sea level
IEC efficiency classifications
For these motors, the IEC 60034-30-1 standard defines four efficiency classes:
IE1: Standard Efficiency
IE2: High Efficiency
IE3: Premium Efficiency
IE4: Super-premium Efficiency
The actual efficiency values required to meet each class (IE1, IE2, etc.) depend on the motor’s operating frequency, number of poles, and rated output, as shown in the example below.
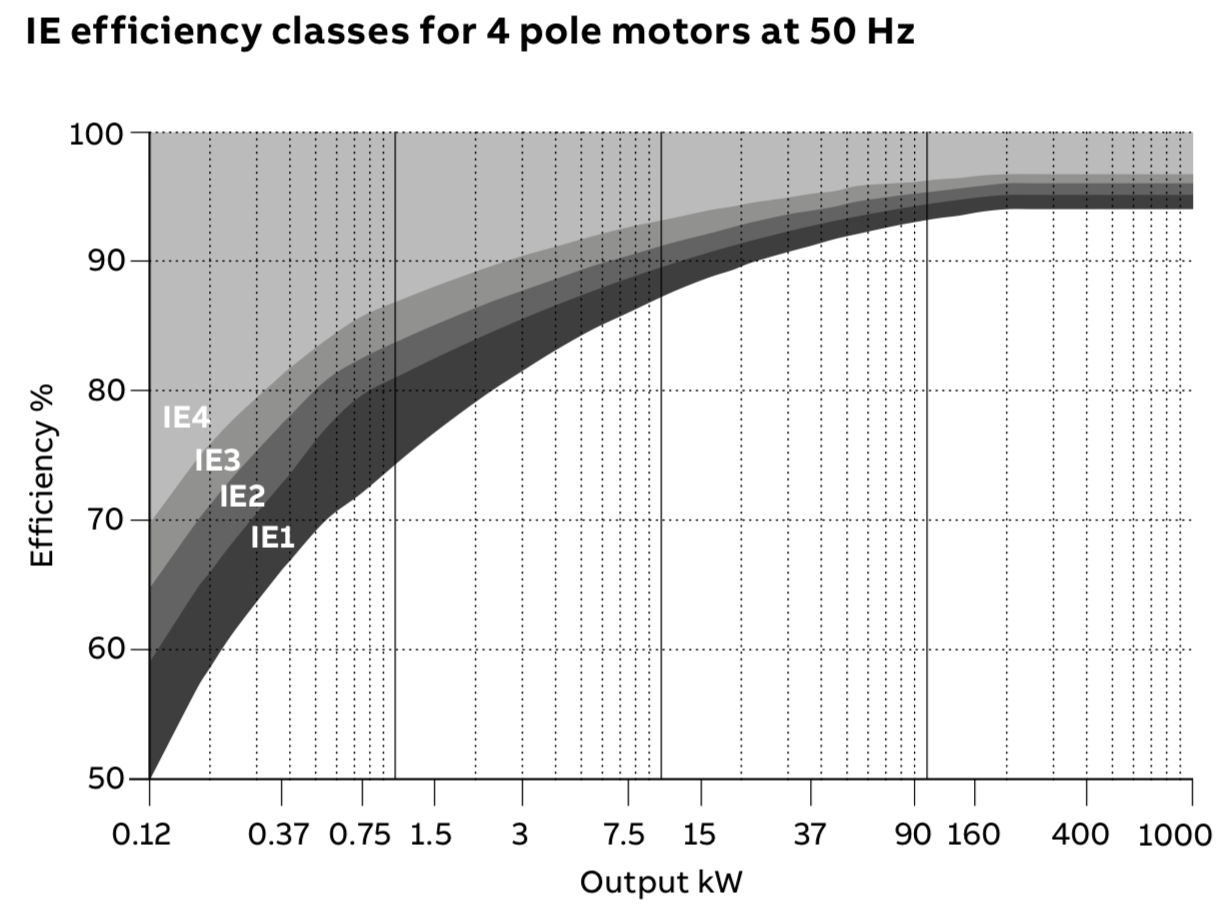
Image credit: ABB
Although much work has been done by the IEC to create a single, harmonized standard, some countries and regions still use local efficiency standards. But in many cases, the IEC efficiency levels overlap with local standards. Case in point: In the U.S., NEMA efficiency standards for electric motors are still widely used, but for more than 95 percent of ratings, the NEMA premium classification is identical to the IEC classification of IE3.
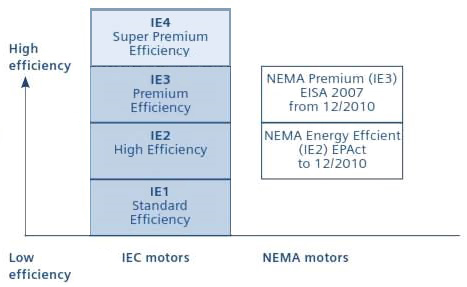
For most induction motors rated from 0.75 to 357 kW, the U.S. MEPS is NEMA premium, and the EU MEPS is IE3 — making the required efficiency essentially the same in both regions.
Whether defined by IEC, NEMA, JEMA, or other agencies, efficiency standards allow manufacturers and purchasers of electric motors to quantify efficiency, removing ambiguity and disparities in ratings among manufacturers. It also allows users to meet the MEPS required in their region or country, regardless of the origin of the motor.
Filed Under: Motion Control Tips




