
Rice University graduate student Sruthi Radhakrishnan shows samples of pure hexagonal boron nitride and fluorinated hexagonal boron nitride. Image credit: Jeff Fitlow/Rice University
A little fluorine turns an insulating ceramic known as white graphene into a wide-bandgap semiconductor with magnetic properties. Rice University scientists said that could make the unique material suitable for electronics in extreme environments.
A proof-of-concept paper from Rice researchers demonstrates a way to turn two-dimensional hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) – aka white graphene – from an insulator to a semiconductor. The magnetism, they said, is an unexpected bonus.
Because the atomically thin material is an exceptional conductor of heat, the researchers suggested it may be useful for electronics in high-temperature applications, perhaps even as magnetic memory devices.
The discovery appears this week in Science Advances.
“Boron nitride is a stable insulator and commercially very useful as a protective coating, even in cosmetics, because it absorbs ultraviolet light,” said Rice materials scientist Pulickel Ajayan, whose lab led the study. “There has been a lot of effort to try to modify its electronic structure, but we didn’t think it could become both a semiconductor and a magnetic material.
“So this is something quite different; nobody has seen this kind of behavior in boron nitride before,” he said.
The researchers found that adding fluorine to h-BN introduced defects into its atomic matrix that reduced the bandgap enough to make it a semiconductor. The bandgap determines the electrical conductivity of a material.
A density functional theory calculation showed the magnetic properties of a fluorinated sample of hexagonal boron nitride. This version is anti-ferromagnetic, determined by how the fluorine atoms (red) attach to the boron and nitrogen matrix. Credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University
“We saw that the gap decreases at about 5 percent fluorination,” said Rice postdoctoral researcher and co-author Chandra Sekhar Tiwary. The gap gets smaller with additional fluorination, but only to a point. “Controlling the precise fluorination is something we need to work on. We can get ranges but we don’t have perfect control yet. Because the material is atomically thin, one atom less or more changes quite a bit.
“In the next set of experiments, we want to learn to tune it precisely, atom by atom,” he said.
They determined that tension applied by invading fluorine atoms altered the “spin” of electrons in the nitrogen atoms and affected their magnetic moments, the ghostly quality that determines how an atom will respond to a magnetic field like an invisible, nanoscale compass.
“We see angle-oriented spins, which are very unconventional for 2-D materials,” said Rice graduate student and lead author Sruthi Radhakrishnan. Rather than aligning to form ferromagnets or canceling each other out, the spins are randomly angled, giving the flat material random pockets of net magnetism. These ferromagnet or anti-ferromagnet pockets can exist in the same swatch of h-BN, which makes them “frustrated magnets” with competing domains.
The researchers said their simple, scalable method can potentially be applied to other 2-D materials. “Making new materials through nanoengineering is exactly what our group is about,” Ajayan said.
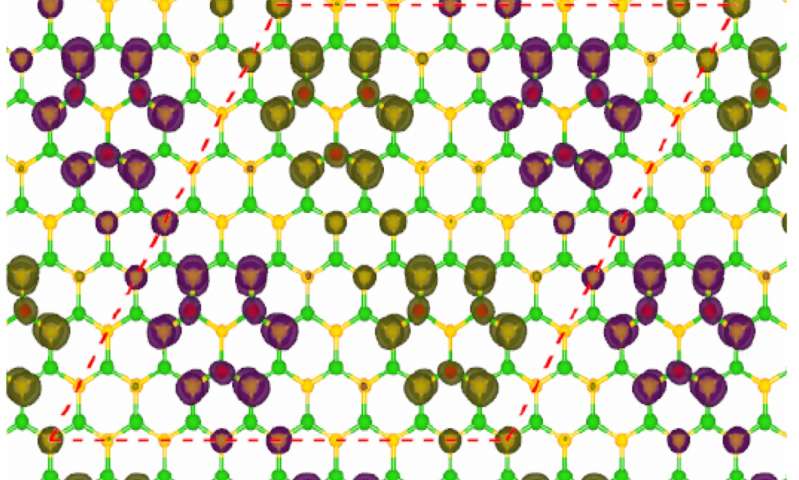
A density functional theory calculation showed the magnetic properties of a fluorinated sample of hexagonal boron nitride. This version is anti-ferromagnetic, determined by how the fluorine atoms (red) attach to the boron and nitrogen matrix. Image credit: Ajayan Group/Rice University
Co-authors of the paper are graduate students Carlos de los Reyes and Zehua Jin, chemistry lecturer Lawrence Alemany, postdoctoral researcher Vidya Kochat and Angel Martí, an associate professor of chemistry, of bioengineering and of materials science and nanoengineering, all of Rice; Valery Khabashesku of Rice and the Baker Hughes Center for Technology Innovation, Houston; Parambath Sudeep of Rice and the University of Toronto; Deya Das, Atanu Samanta and Rice alumnus Abhishek Singh of the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore; Liangzi Deng and Ching-Wu Chu of the University of Houston; Thomas Weldeghiorghis of Louisiana State University and Ajit Roy of the Air Force Research Laboratories at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base.
Ajayan is chair of Rice’s Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry.
Filed Under: Materials • advanced




