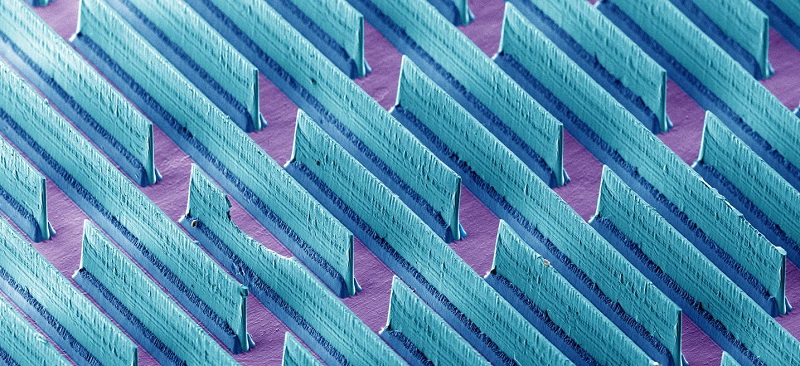
This is a microscopic image showing the walls formed to mimic the adhesion characteristics of gecko feet. Image credit: Georgia Tech
A gecko scampering up a wall or across a ceiling has long fascinated scientists and encouraged them to investigate how to harness lizard’s mysterious ability to defy gravity.
While human-made devices inspired by gecko feet have emerged in recent years, enabling their wearers to slowly scale a glass wall, the possible applications of gecko-adhesion technology go far beyond Spiderman-esque antics.
A Georgia Institute of Technology researcher is looking into how the technology could be applied in a high-precision industrial setting, such as in robot arms used in manufacturing computer chips.
“There are numerous ways that gecko adhesion could be used in an industrial setting, especially in handling delicate materials like the silicon wafers used in manufacturing computer processors,” said Michael Varenberg, an assistant professor in Georgia Tech’s George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering.
But before robot arms and other devices can implement gecko adhesion technology, researchers need more information about the mechanical and physical characteristics of the human-made adhesive surfaces.
In a study published Dec. 13 in Journal of the Royal Society Interface, Varenberg looked at a particular type of gecko-inspired adhesive surface and narrowed down a range of angles at which the material will attach stronger and release its grip easier.
The gecko gets its unique ability through the use of tiny hairs that interact with surfaces at an intermolecular level. It’s a one-two process during which the tiny film-like hairs are pressed onto the surface and engaged with a shearing action. They then either hold to the surface or easily release when pulled away at different directions.
For that process to be replicated in a factory using man-made adhesive technology, researchers must determine the precise angles at which to apply a load to get or release the grip between the robotic arm and the silicon wafer.
Varenberg’s team tested a wall-shaped microstructure surface molded out of polyvinylsiloxane and designed to mimic the gecko’s attachment ability. Their tests showed that the optimum attachment angle varies between 60 and 90 degrees, while the microstructure detach at zero force when the pull-off angle reaches 140-160 degrees.
“That relatively wide range to control the attachment and pulling away for these wall-shaped microstructures will make it easier to build a mechanical process around that tolerance,” Varenberg said.
That could hold promise for replacing a current method used during the processing and inspection of silicon wafers in computer processor production. Robot arms employ ceramic chucks that use vacuum or electrostatic grippers to pick up and handle the wafers. Soon after installation, the ceramic contact posts start wearing down due to cyclic loading and release particles that can potentially contaminate the backside of the wafer leading to lithography defects on its front side.
“This reality is inconsistent with the cleanliness standards required in the semiconductor industry,” Varenberg said. “Using gecko adhesion microstructures instead would be better because they do not generate any damage to wafers and do not wear over time.”
Next steps in the research include simplifying the manufacturing technique, working with industrial-grade materials as well as studying the effects of environment and surface geometry parameters, Varenberg said.
Filed Under: Materials • advanced




