The additive manufacture of large-volume plastic components is a time-consuming undertaking. Researchers at the Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology IWU have now developed Screw Extrusion Additive Manufacturing (SEAM), a system and process that is eight times faster than conventional 3D printing.
Three-dimensional printers that build small souvenirs layer by layer from melted plastic are often used at tradeshows. It can take up to an hour to produce a pocket-sized souvenir. This process is far too slow for the mass-production of components, as required by the automotive industry, for instance. A system from the Fraunhofer Institute for Machine Tools and Forming Technology IWU in Chemnitz is now taking 3D printing to a new level: The system’s high-speed technology takes only 18 minutes to produce a plastic component that is 30 centimeters high. A team of researchers at the Fraunhofer IWU has developed this technology for the additive manufacture of large-volume resilient plastic components. Tool manufacturers as well as the automotive and aerospace industries benefit from the innovative 3D printer that achieves eight times the process speed. This printer uses the SEAM – short for Screw Extrusion Additive Manufacturing – process developed at the Chemnitz Institute.
How does SEAM achieve these high process speeds?
“By combining machine tool technology with 3D printing,” says Dr. Martin Kausch, a scientist at Fraunhofer IWU. To process the plastic, the researchers use a specially designed unit that melts the raw material and ejects it at a high output rate. This unit is installed above a construction platform that can be swiveled in six axes by using the motion system of a machine tool. “So far, this combination is unique,” says Dr. Kausch. The hot plastic is deposited in layers on the construction platform. The motion system of the machine ensures that the construction panel slides along under the nozzle in such a way that the previously programmed component shape is produced. The table can be moved at a speed of one meter per second in the X-, Y- and Z-axes and can also be tilted by up to 45 degrees. “This enables us to print eight times faster than conventional processes, enormously reducing the production times for plastic components.”
Every hour, up to seven kilograms of plastic are pressed through the hot nozzle with a diameter of one millimeter. Comparable 3D printing processes, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Modeling (FLM), usually achieve only 50 grams of plastic per hour. A unique feature is that, instead of expensive FLM filament, SEAM processes free-flowing, cost-effective standard plastic granulate into resilient, fiber-reinforced components that are several meters in size. This method allows material costs to be reduced by a factor of two hundred.
SEAM allows researchers to implement complex geometries without supporting structures. The highlight is that the new system even makes it possible to print on existing injection-molded components. “As our construction platform can be swiveled, we are able to print on curved structures with a separately moving Z-axis,” says Kausch. “In tests, we were able to process a wide variety of plastics. They ranged from thermoplastic elastomers to high-performance plastics with a 50 percent content of carbon fiber. These plastics are materials that are particularly relevant to industry and cannot be processed with traditional 3D printers.”
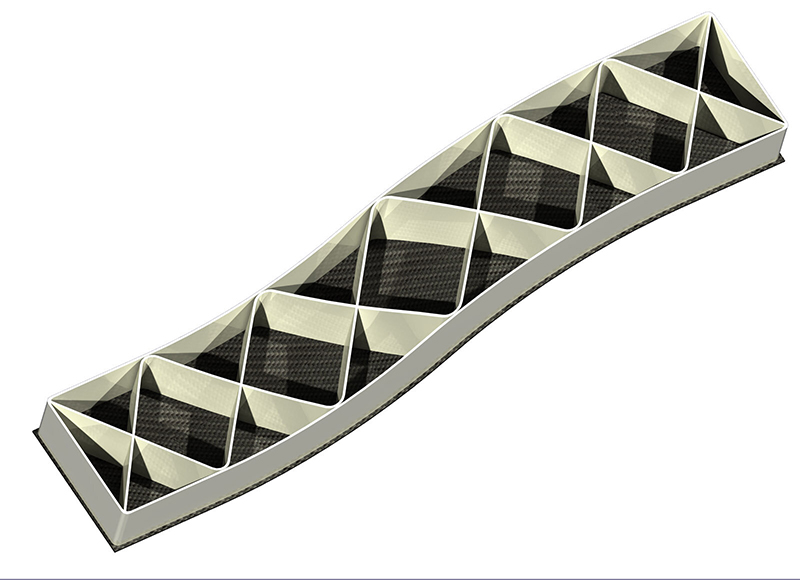
This experimental component is a hybrid of CFRP sheet metal and 3D printed structures – SEAM makes it possible to print on injection-molded components or sheet metal for the first time. Credit: Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft
Filed Under: 3D printing • additive • stereolithography, Product design




