Smart phones autocorrect in texting, search engines autocomplete queries, and mapping applications redirect navigation in real-time to avoid slowed traffic. These ubiquitous AI-based technologies adapt to everyday needs and learn user habits by focusing on making the algorithm better, but Army researchers want to enhance AI by providing more information about the intent of the user.
New research published in Science Advancestoday looks at Soldier brain activity during specific tasks for ways to incorporate AI teaming to dynamically complete tasks.
The Army envisions a future battlefield wrought with teams of Soldiers and autonomous systems, and as part of this future vision, the Army is looking to create technologies that can predict states and behaviors of the individual to create a more optimized team, said Dr. Jean Vettel, a senior neuroscientist at the Combat Capabilities Development Command Army Research Laboratory, the Army’s corporate research laboratory also known as ARL.
Recent collaborative work between ARL and the University at Buffalo is looking at ways the dynamics and architecture of the human brain may be coordinated to predict such behaviors and consequently optimize team performance.
“While this research focuses on a single person, the purpose is to understand how an individual’s brain activity can be used to create novel strategies for a teaming environment, both for teams with Soldiers as well as teams with Autonomy” said Vettel, a co-author of the recent paper.
“In military operations, Soldiers perform multiple tasks at once. They’re analyzing information from multiple sources, navigating environments while simultaneously assessing threats, sharing situational awareness, and communicating with a distributed team. This requires Soldiers to constantly switch among these tasks, which means that the brain is also rapidly shifting among the different brain regions needed for these different tasks,” Vettel said. “If we can use brain data in the moment to indicate what task they’re doing, AI could dynamically respond and adapt to assist the Soldier in completing the task.”
To achieve this future capability, the researchers first sought to understand how the brain coordinates its different regions while executing a particular task. They used a computational approach to understand how this may be characterized to inform the behavioral prediction.
To complete the study, researchers mapped how different regions of the brain were connected to one another in 30 different people via tracts of tissue called white matter. (The specific connectivity pattern linking different brain regions varies between individuals.)
Next, the scientists converted these maps into computational models of each subject’s brain, and used computers to simulate what would happen when a single region of a person’s brain was stimulated. The researchers then used a mathematical framework, which they developed, to measure how brain activity became synchronized across various cognitive systems in the simulations.
“The brain is very dynamic,” Dr. Kanika Bansal, lead author on the work, says. “Connections between different regions of the brain can change with learning or deteriorate with age or neurological disease. Connectivity also varies between people. Our research helps us understand this variability and assess how small changes in the organization of the brain can affect large-scale patterns of brain activity related to various cognitive systems.”
While Dr. Bansal points out the foundational principles of brain coordination this research describes, the method described in the work could potentially be extended outside the brain, as well, creating dynamic teaming assignments in the future.
“While the work has been deployed on individual brains of a finite brain structure, it would be very interesting to see if coordination of Soldiers and autonomous systems may also be described with this method, too,” Dr. Javier Garcia, ARL neuroscientist and co-author points out. “Much how the brain coordinates regions that carry out specific functions, you can think of how this method may describe coordinated teams of individuals and autonomous systems of varied skills work together to complete a mission.”
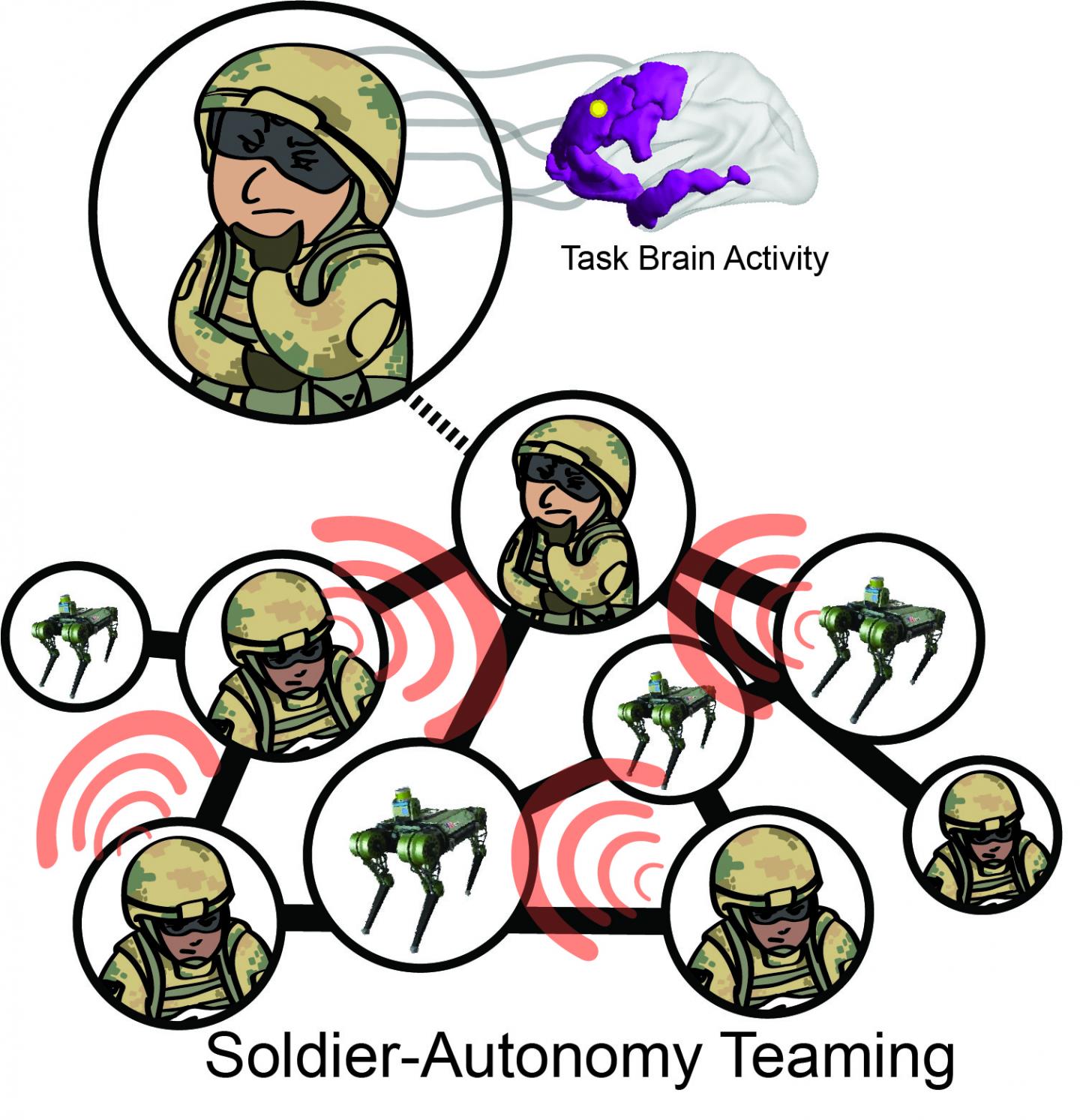
Army researchers are looking for ways to use brain data in the moment to indicate specific tasks Soldiers are performing. This knowledge, they say, will better enable AI to dynamically respond and adapt to assist the Soldier in completing the task. (Image Source: US Army graphic)
Filed Under: Aerospace + defense, Robotics • robotic grippers • end effectors




