Rapid advancement towards digital transformation will position digital twins as crucial elements for businesses worldwide.
By Saloni Walimbe, Global Market Insights Inc.
The digital revolution is making its way across the industrial world at a breakneck pace. Various industrial sectors are adapting to this evolution by integrating key technologies like AI (artificial intelligence), VR (virtual reality), and AR (augmented reality), among others into their workflows, processes, and products. According to the Digital Marketing Institute, nearly 27% of managers consider digitization to be a tool for business survival.
Among the vast array of technologies being leveraged as solutions for digital transformation, digital twin technology is gaining increasing favor worldwide from major entities working to establish a firm presence in the modern digital ecosystem.
Digital twins, also known as digital replicas or virtual twins, refer to a digital copy of any physical process, system, or product. This technology helps bridge the gap between physical and virtual environments, by collecting data regarding physical elements through the use of sensors in real-time. These data are then used to replicate the element in digital form, creating a plethora of opportunities for businesses to analyze, understand, control, and optimize their operations.
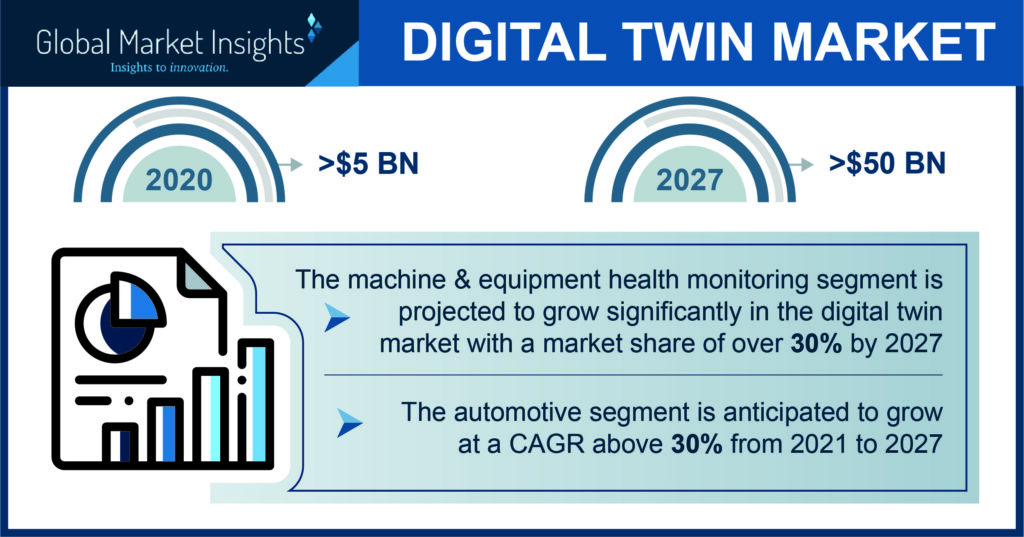
Hailed as one of the most disruptive technologies of the decade, the digital twin industry, is anticipated to cross $50 billion by 2027 and will likely be a major driver for the digital revolution worldwide.
Hailed as one of the most disruptive technologies of the decade, the digital twin industry, which is anticipated to cross $50 billion by 2027 based on Global Market Insights Inc. reports, will likely be a major driver for the digital revolution worldwide.
Why is digital twin important for industrial IIOT?
Industry 4.0, or the fourth Industrial Revolution visualizes a highly connected world reliant on smart technologies, all designed to communicate with one another using the emerging IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) concept. In order for this concept to work, a standard approach is needed to understand the description of key components and the way they interact with other assets or components in a smart machine; i.e., a digital twin. While still in the nascent stage, these precise digital models are expediting digital transformation, not just in the industrial sector but nearly everywhere.
COVID-19 has added further relevance to this technology over the past year, underpinning its importance in crucial tasks such as automated processing, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
The potential benefits of the digital twin industry are vast, from reducing design and build times for machines, to optimizing performance throughout the operational life cycle to playing a prominent role in predictive maintenance, smart maintenance, and condition monitoring. Using digital replicas, engineers can merge product data with important application data to deliver comprehensive insights, and when combined with technologies like AI, forecast future performance with accuracy.
3 ways digital twin technology is helping industrial automation design
Over the years, the industrial world has been witnessing a marked shift towards progress through technological innovation. The emergence of critical Industry 4.0 enablers like wireless connectivity, AI, and automation facilitates the extraction of valuable data and the delivery of real-time performance insights. Digital twin technology can help engineers to use these insights in many ways and allow them to improve operational performance across the industrial floor.
Bridging gaps between physical and virtual environments
Digital replicas can help enterprises by creating holograms or digital visualizations of physical models to bridge the gap between the digital and physical environment, particularly in combination with AR/VR (augmented reality/virtual reality), IoT, and AI/ML. The technology facilitates virtual collaboration, intake of sensor data, speedy simulation of various situations, better comprehension of what-if scenarios, and more precise prediction of results, which can be used to control elements in the physical world. Digital twin simulations and leading Industry 4.0 technologies like AI, and 5G are becoming more closely associated with the emergence of novel spatial platforms designed to give engineers more immersive access to virtual replicas of their environments.
For instance, in April 2021, UK-based vehicle battery producer Hyperbat partnered with Ericsson, BT, and Nvidia to develop the first 5G, VR (virtual reality) digital twin solution in the world. The objective behind this move was to enhance the collaboration between the remote teams of Hyperbat in the UK, through an interactive virtual 3D engineering model, allowing the firms to accelerate the production process for electric and hybrid vehicles. The 5G VR digital twin technology, powered by technologies like CloudXR, NVIDIA RTX Virtual Workstation software, and NVIDIA RTX technology, can be used to facilitate real-time immersive experiences for teams, both remotely and on the production floor.
Undertaking timely predictive maintenance activities
Another way digital twins are able to transform the ways industries operate is by facilitating the implementation of predictive maintenance. With the emergence of virtual twins and IoT, businesses worldwide are shifting towards advanced predictive maintenance models designed to optimize the maintenance cycle and create a balance between preventative and corrective maintenance activities. essentially, digital replicas can convert real-world data pertaining to physical systems, inputs, or objects into simulations or predictions, to show the impact of these inputs on the physical system.
To that end, Siemens Energy enlisted NVIDIA’s Omniverse platform in November 2021, to develop digital twins designed to support predictive maintenance of power plants. The digital replica technology developed by NVIDIA will help the company create a new workflow to mitigate planned shutdown frequencies through physics-based real-time simulations of steam and water in HRSGs (heat recovery steam generators), whilst ensuring optimum security.
Increasing operational efficiencies
The application scope of the digital twin market is growing rapidly in recent years. In smart city development, especially, digital twin technology is playing an increasingly crucial role in the more precise designing of buildings and infrastructure, in order to circumvent the need for costly modifications afterward. Additionally, digital replicas can help engineers decrease the cost of emergency response and integrate green building design options to facilitate energy savings in the long run.
In smart city planning, digital twins make use of physical models, sensor data, and input data to replicate and simulate the performance of the structures over their corresponding physical twin’s lifecycle. For this reason, the technology is hailed by many city governments and urban planners as the ultimate tool for cost-friendly infrastructure designing and development.
The ability to run simulations on the basis of large datasets makes digital twin technology an important asset in smart city initiatives. Testament to this is the partnership of the researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory and the Energy Department’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory with Chattanooga, on the use of digital replicas to enhance energy efficiency, whilst optimizing the speed, safety, and travel time for drivers.
With digital twins, businesses can reduce their maintenance expenses to a great extent. As a result of this new technology, the industry will benefit from enhanced revenues and a reduction of unwanted overheads that arise from problems with equipment and processes. Additionally, it streamlines and improves the production line in an organization and in turn improves customer service, which is the ultimate goal of any industry. Overall, it can be stated that the digital twin, a cutting-edge trend in technology, will play a vital role in industrial IoT application deployments.
Filed Under: IoT • IIoT • Internet of things • Industry 4.0, DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION (DX)




