These six infrared images of Saturn’s moon Titan represent some of the clearest, most seamless-looking global views of the icy moon’s surface produced so far. The views were created using 13 years of data acquired by the Visual and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) instrument on board NASA’s Cassini spacecraft. The images are the result of a focused effort to smoothly combine data from the multitude of different observations VIMS made under a wide variety of lighting and viewing conditions over the course of Cassini’s mission.
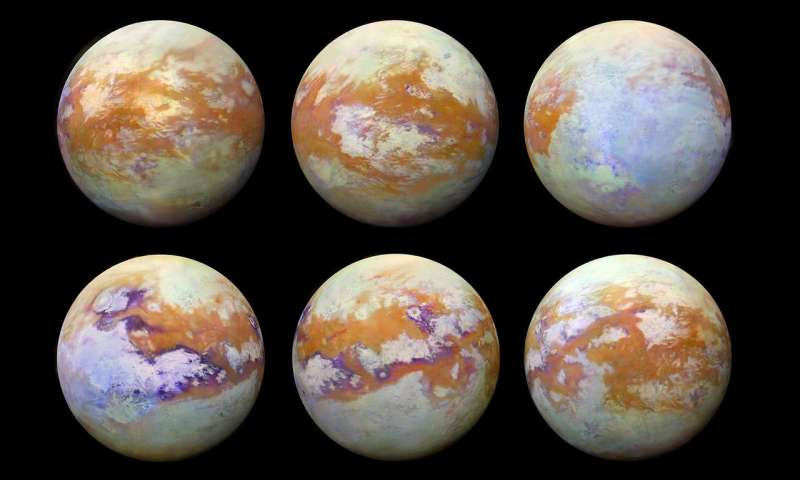
(Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Stéphane Le Mouélic, University of Nantes, Virginia Pasek, University of Arizona)
Previous VIMS maps of Titan (for example, PIA02145) display great variation in imaging resolution and lighting conditions, resulting in obvious seams between different areas of the surface. With the seams now gone, this new collection of images is by far the best representation of how the globe of Titan might appear to the casual observer if it weren’t for the moon’s hazy atmosphere, and it likely will not be superseded for some time to come.
Observing the surface of Titan in the visible region of the spectrum is difficult, due to the globe-enshrouding haze around the moon. This is primarily because small particles called aerosols in Titan’s upper atmosphere strongly scatter visible light. But Titan’s surface can be more readily imaged in a few infrared “windows”—infrared wavelengths where scattering and absorption of light is much weaker. This is where the VIMS instrument excelled, parting the haze to obtain clear images of Titan’s surface. (For comparison, Figure B shows Titan as it appears in visible light, as does PIA11603.
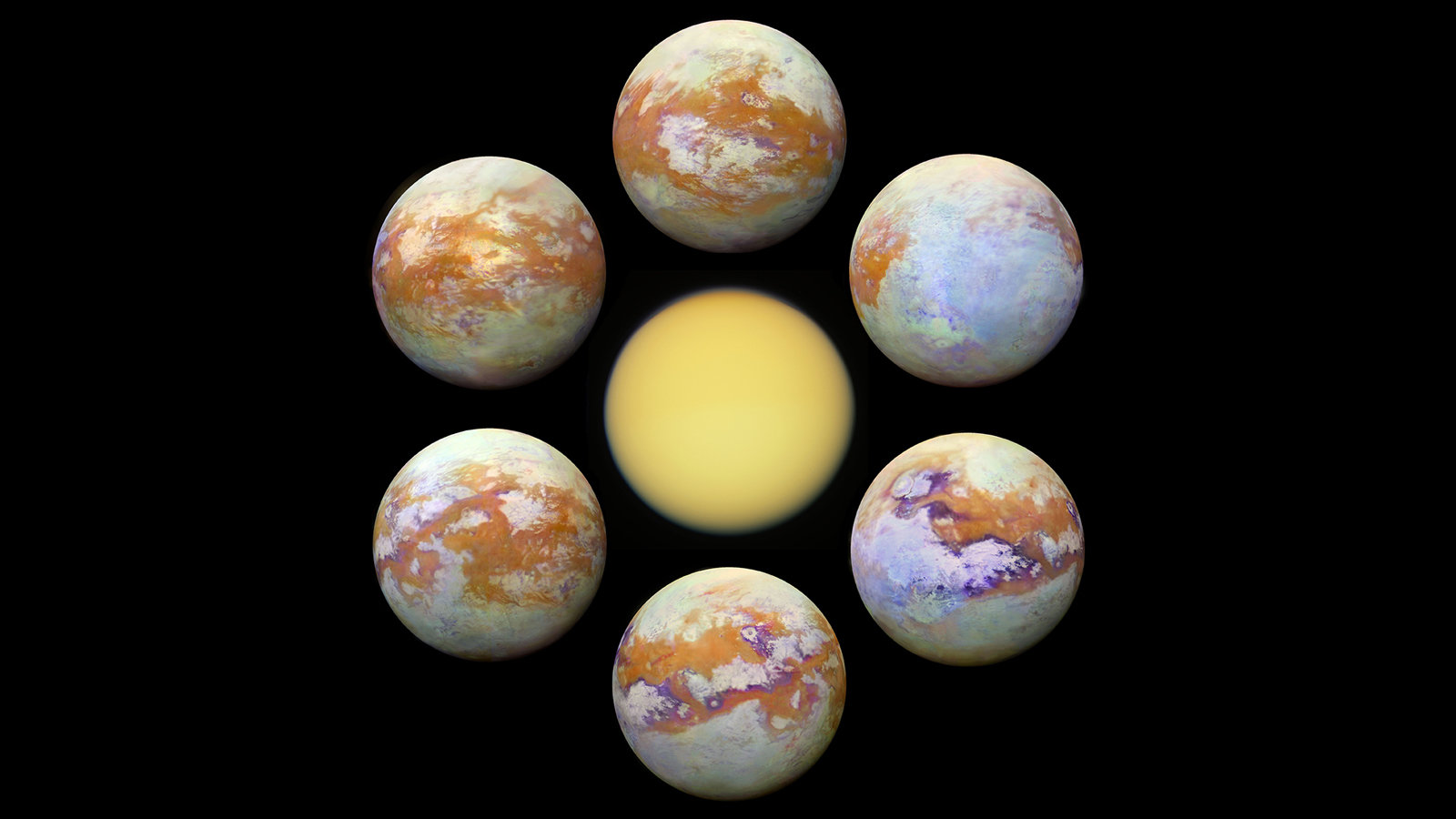
Figure B. (Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Stéphane Le Mouélic, University of Nantes, Virginia Pasek, University of Arizona)
Making mosaics of VIMS images of Titan has always been a challenge because the data were obtained over many different flybys with different observing geometries and atmospheric conditions. One result is that very prominent seams appear in the mosaics that are quite difficult for imaging scientists to remove. But, through laborious and detailed analyses of the data, along with time consuming hand processing of the mosaics, the seams have been mostly removed. This is an update to the work previously discussed in PIA20022.
Any full color image is comprised of three color channels: red, green and blue. Each of the three color channels combined to create these views was produced using a ratio between the brightness of Titan’s surface at two different wavelengths (1.59/1.27 microns [red], 2.03/1.27 microns [green] and 1.27/1.08 microns [blue]). This technique (called a “band-ratio” technique) reduces the prominence of seams, as well as emphasizing subtle spectral variations in the materials on Titan’s surface. For example, the moon’s equatorial dune fields appear a consistent brown color here. There are also bluish and purplish areas that may have different compositions from the other bright areas, and may be enriched in water ice.
For a map of Titan with latitudes, longitudes and labeled surface features, see PIA20713.
It is quite clear from this unique set of images that Titan has a complex surface, sporting myriad geologic features and compositional units. The VIMS instrument has paved the way for future infrared instruments that could image Titan at much higher resolution, revealing features that were not detectable by any of Cassini’s instruments.
Filed Under: Aerospace + defense




