By Laura Carrabine, Senior Editor
Many of the design requirements for NASA’s latest Mars explorer Curiosity are related to the Sample Acquisition and Sample Processing and Handling (SASPaH) subsystem that will gather soil samples from Mars’ surface. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) collaborated with Helical Products Company engineers to develop flexible couplings and machined springs to achieve the sampling and testing tasks.
The flexible coupling will be part of the vibration mechanism located at the front of the rover. Vibration, aided by the flexible coupling, is used to pass the powder through sifters and the sampling system. Then, the particles are processed and examined with the rover’s analytical instruments.
In addition to flexible couplings, Curiosity is equipped with several Helical machined springs. These devices are used as a locking latch in the rocket-deploy pivot mechanism. Once the rover is deployed on Mars the pivot will rotate and the latch will lock it in place.
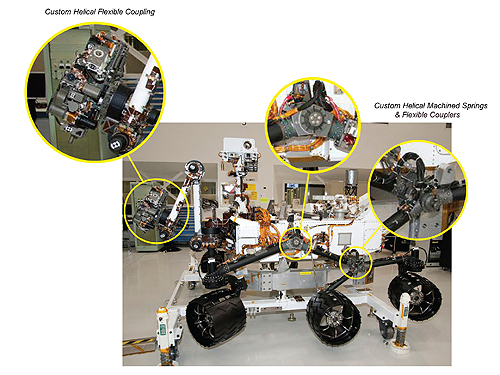
Highlighted in this image are several areas where Helical’s couplings and machined springs are located on the Mars Curiosity vehicle.
Helical engineers designed the spring to meet compression and lateral translation spring rates, end attachments, and titanium material for its lightweight characteristic. Application engineer Michael Haber said, “The double-start flexure adds redundancy and confidence that the spring will operate the latch. The spring also showcases the advantage of Helical technology to combine a number of components and features into one part which further increases reliability – a major concern for Curiosity since parts won’t be serviceable.”
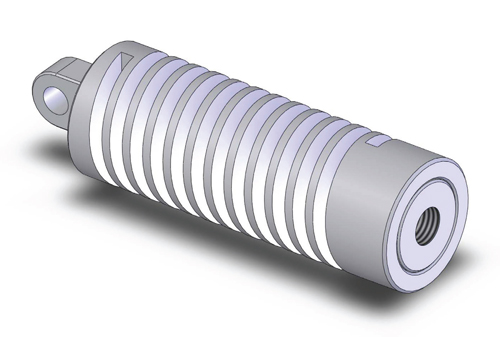
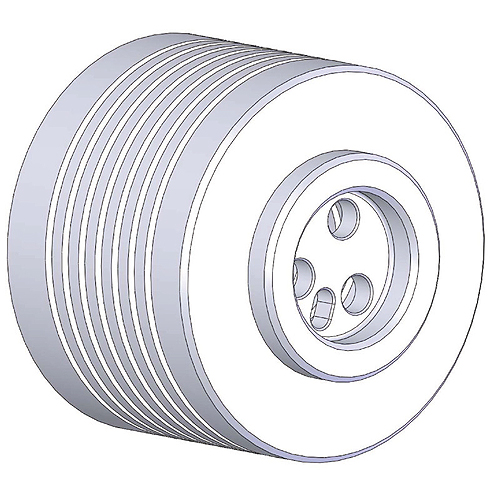
This custom machined spring is a critical component in the locking mechanism of an articulating arm on the Mars Rover. The purpose of the arm is to be able to pick up samples or materials from Mars’ surface.
According to Matthew Bush, Helical’s application engineer responsible for the flexible coupling design, “I worked with JPL and our analyst Gary Boehm on calculations and design of this coupling for approximately five months before we started to manufacture the parts. The engineers at JPL wanted to make certain that they evaluated every aspect of our part and how it affects the overall system.”

The flexible shaft coupling is part of the vibration mechanism found in the Vibration Sample Acquisition and Sample Processing and Handling subsystem and is located at the end of the robotic arm.
This rover is the biggest one yet to roam the red planet and reached the size of an automobile. Curiosity will be joining Mars Opportunity which has been exploring the planet since January 2004. The rover is scheduled to land on August 6, 2012 in the Gale crater. Once landed, the vehicle will begin its two-year mission of examining soil at the base of a nearby mountain that suggests water once existed and the possibility of life.
Helical components comprise other space projects including springs on the original Mars “Sojourner” rover, and parts for the International Space Station and the Hubble Space Telescope.
Helical Products Company, Inc.
www.heli-cal.com
Filed Under: Aerospace + defense, Couplings, The Robot Report, MORE INDUSTRIES, Motion control • motor controls, Mechatronics





Tell Us What You Think!